- PRODUCT DETAIL
- User Also Buy
- PRINCIPLE
- Demo Video
- Surface Area Analyzer FAQs
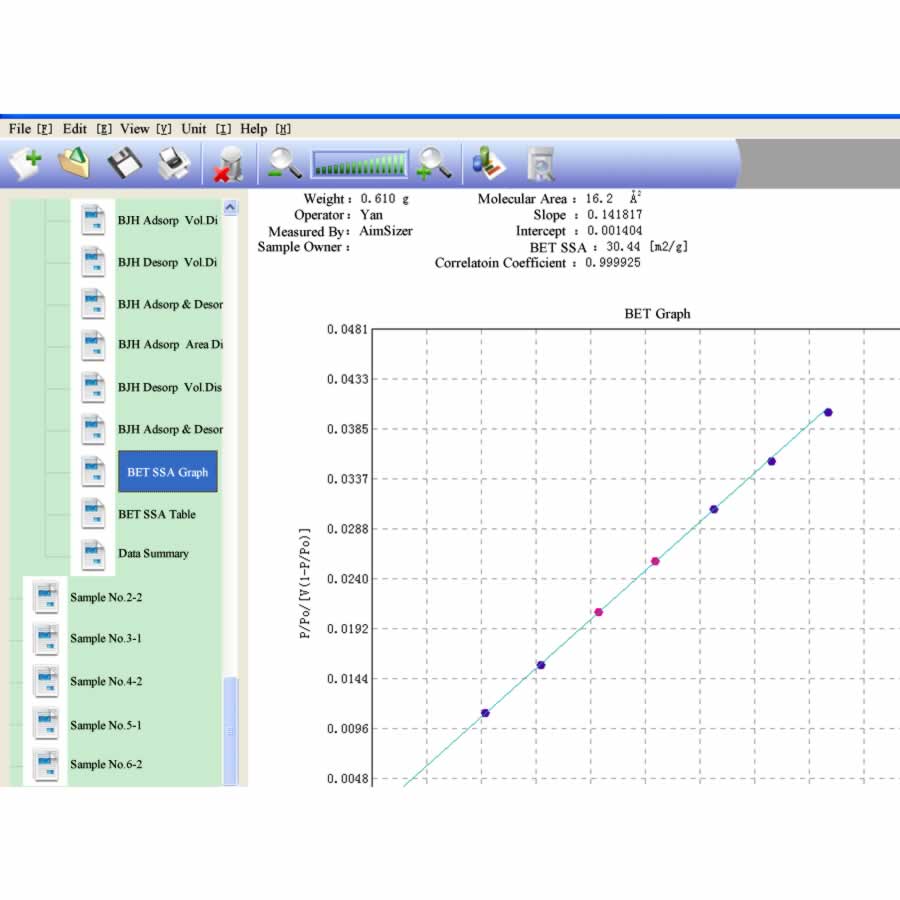
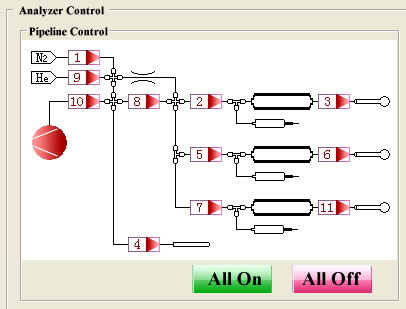
AS-3012 BET Surface Area Analyzer performs surface area analysis on ISO 9277. ISO 9277 is about determination of the specific surface area of solids by gas adsorption using the BET method. AS-3012 BET surface area analysis instrument works on the principle of the popular physical adsorption isotherms, specifically static volumetric method.The computer controls the operation automatically without any human monitoring. AS-3012 analyzes two samples at the same time inWindows system.The instrument can perform a single point, multi-point BET surface area, BJH mesoporous, pore distribution, pore size and total pore volume and area, and the average pore size. The specific surface area range is from 0.01m 2 / g to no limit. The pore size range is from 0.35nm to 400nm. AS-3012 is widely used in many applications.
- Reference Material
- Gas Regulator
- Sample Tube
- Glass filler rod
- Powder Funnel
- O-ring
- Dewar
- Vacuum Pumps
- Software (English)



| • Specifications of AS-3012 BET Surface Area Analyzer | |||
| • Features of AS-3012 BET Surface Area Instrument | |||
| • Applications of AS-3012 BET Surface Analyzer |
User Also Buy
- HMK-200 Air Jet Sieve - particle size distribution sieve anaysis
- HMK-22 Fisher Sub Sieve Sizer - measures average particle size of powders
- LABULK 0335 Tap Density Tester - measures tapped density of powders
- AS-300 Hall Flowmeter - measures flow rate of powders
- HMKDivider 2001 Rotary Sample Divider - divide powder into several representative portions
PRINCIPLE
The method specified involves the determination of the amount of adsorbate or adsorptive gas required to cover the external and the accessible internal pore surfaces of a solid with a complete monolayer of adsorbate. This monolayer capacity can be calculated fro the adsorption isotherm using the BET equation. Any gas may be used, provided it is physically adsorbed by weak bonds at the surface of the solid (van der Walls forces), and can be desorbed by a decrease in pressure at the same temperature.

Nitrogen at its boiling point (about 77 K) is usually the most suitable adsorptive. If the sensitivity of the instrument when using nitrogen is insufficient for low surface areas, adsorptives of heavier molecules or of vapour pressure lower than nitrogent, e.g. krypton, may be used. The results of measurements with different adsorptives may deviate from each other because of different molecular areas, different accessibilities to pores and different measuring temperatures.
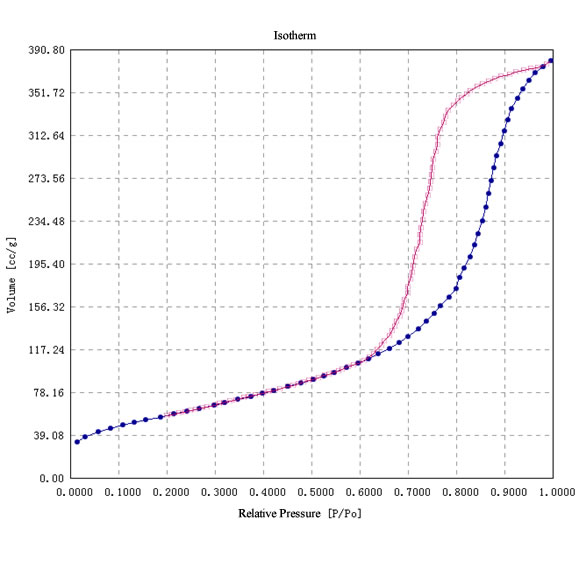
The adsorptive gas is admitted to the sample container which is held at a constant temperature. The amounts adsorbed are measured in equilibrium with the adsorptive gas pressure p and plotted against relative pressure, p/p0, to give an adsorption isotherm. Adsorption isotherms may be obtained by volumetric, gravimetric, calorimetric or spectroscopic measurement or by the carrier gas method using continuous or discontinuous operation.
| Volumetric method | |||
| In order to determine the adsorption isotherm volumetrically by the discontinuous method, known amounts of adsorptive are admitted stepwise into the sample container. At each step, adsorption of the gas by the sample occurs and the pressure in the confied volume falls until the adsorbate and the adsorptive are in equilibrium. The adsorbed volume may be compensated by the introduction of calibrated increments of gas so that the pressure remains constant. The amount of gas adsorbed is the difference between the amount of gas admitted and the amount of gas filling the dead volume (free space in the sample container, including connections), which is determined by application of the general gas equation. The various volumes of the apparatus and their temperatures should be taken into account. | |||
| The dead volume must be determined before or after the measurement of the adsorption isotherm. The calibration is done volumetrically using helium at the measuring temperature. It should be noted that some materials may absorb helium. In this case, corrections can be made after measuring the helium isotherms. During sample measurement and determination of the dead volume, it is recommended that the liquid level in the cooling bath be maintained, unless otherwise compensated, at least 50 mm above the sample and constant to within 1 mm. The determination of the dead volume may be avoided using difference measurements, i.e. by means of reference and sample tubes connected by a differential transducer. | |||
| In the continuous volumetric measurement, the amount of admitted adsorptive may be calculated from the pressure difference and the duration of the gas flow through a calibrated capillary or metering valve. |
Demo Video
http://youtu.be/tZu6cywIumY
Surface Area Analyzer FAQs
- Adsorption
- What is adsorption isotherms?
- What is surface area in BET analysis?
- What is adsorbate in BET analyser?
- What is adsorbent in BET surface analysis?
- What is adsorbent in BET analysis?
- What is adsorptive in surface area analysis?
- What is physisorption for a BET analyzer?
- What is adsorption in surface analysis?